Learning Module 2 - Progressive Web Apps
Introduction
For my fourth project, I was asked to create a progressive web app. For the progressive web app, I made
an installable image gallery. I learned how to use a service worker, web app manifest, and
beforeintallprompt. Along with learning about these new concepts to make a PWA I also had to make the
page responsive so the PWA could be installed on screen sizes ranging from phones to desktops.
Scoring Guide
Here is the scoring guide for my Progressive Web App Webpage: Progressive Web App
Scoring Guide
Responsive Design
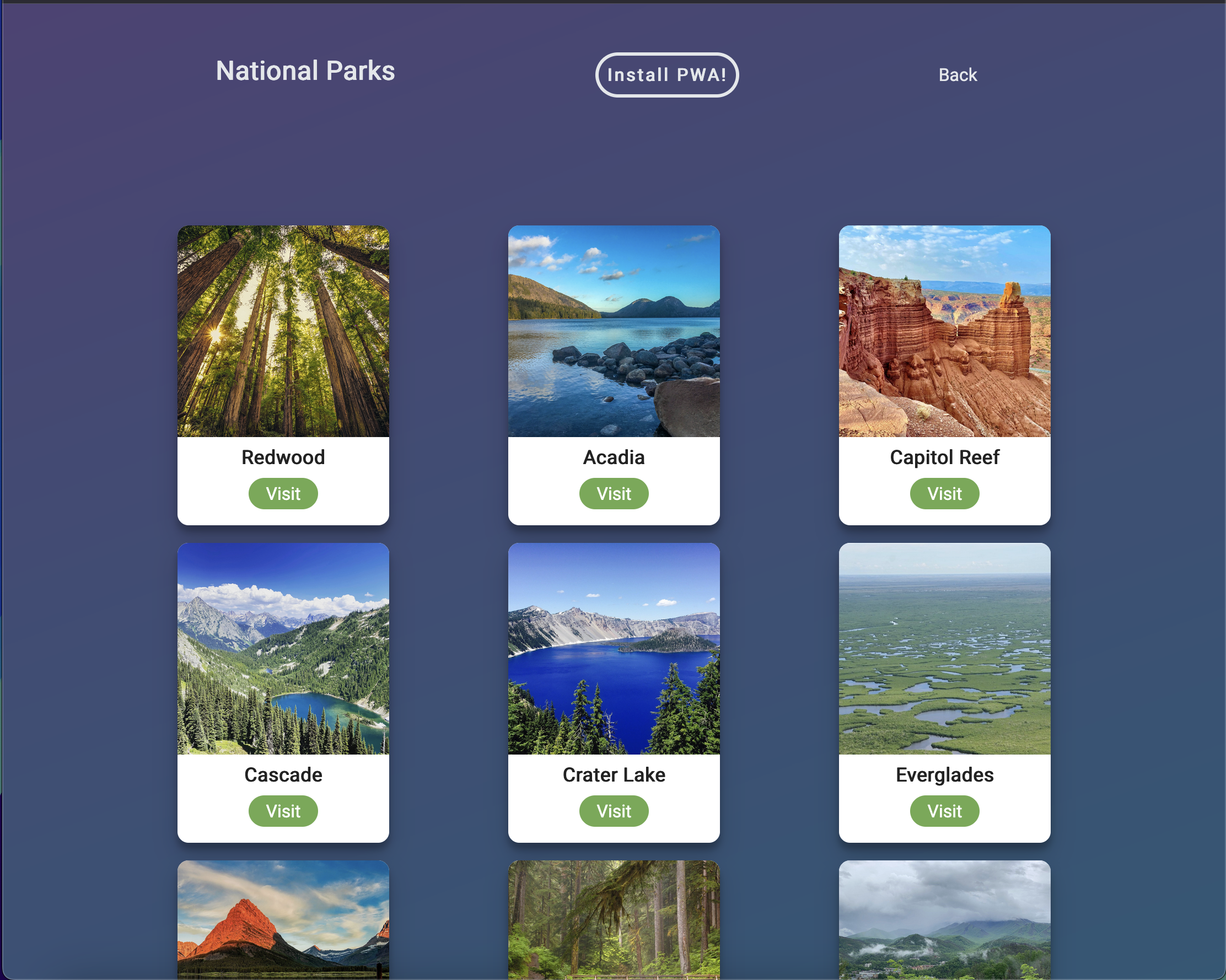
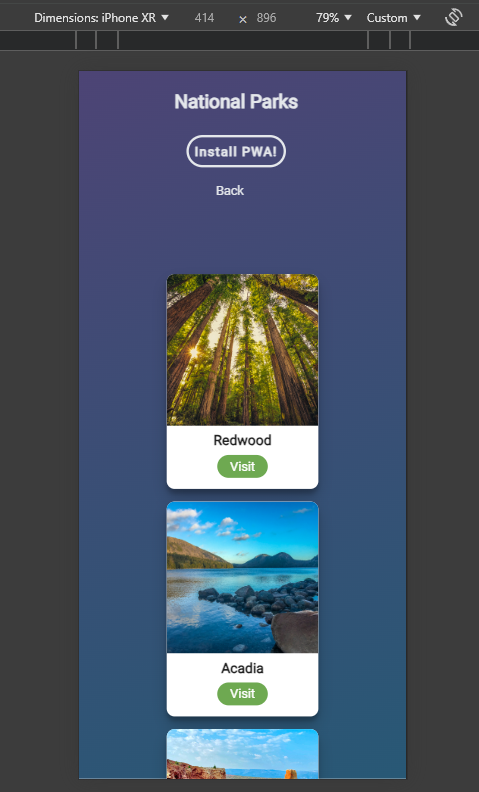
Progressive Web Apps(PWA) are supposed to be designed to be used on various devices. From desktop
computers to cell phones and everything in between a PWA should function on all of them. To make the
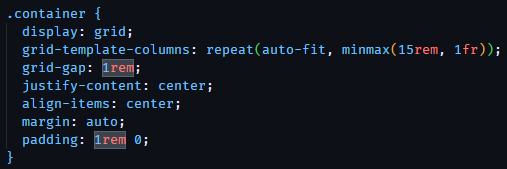
page for my PWA responsive I used a CSS grid to make the image cards. Using CSS Grid allows the
images within the container to shrink from three columns down to one column depending on the screen
size.
Service Worker
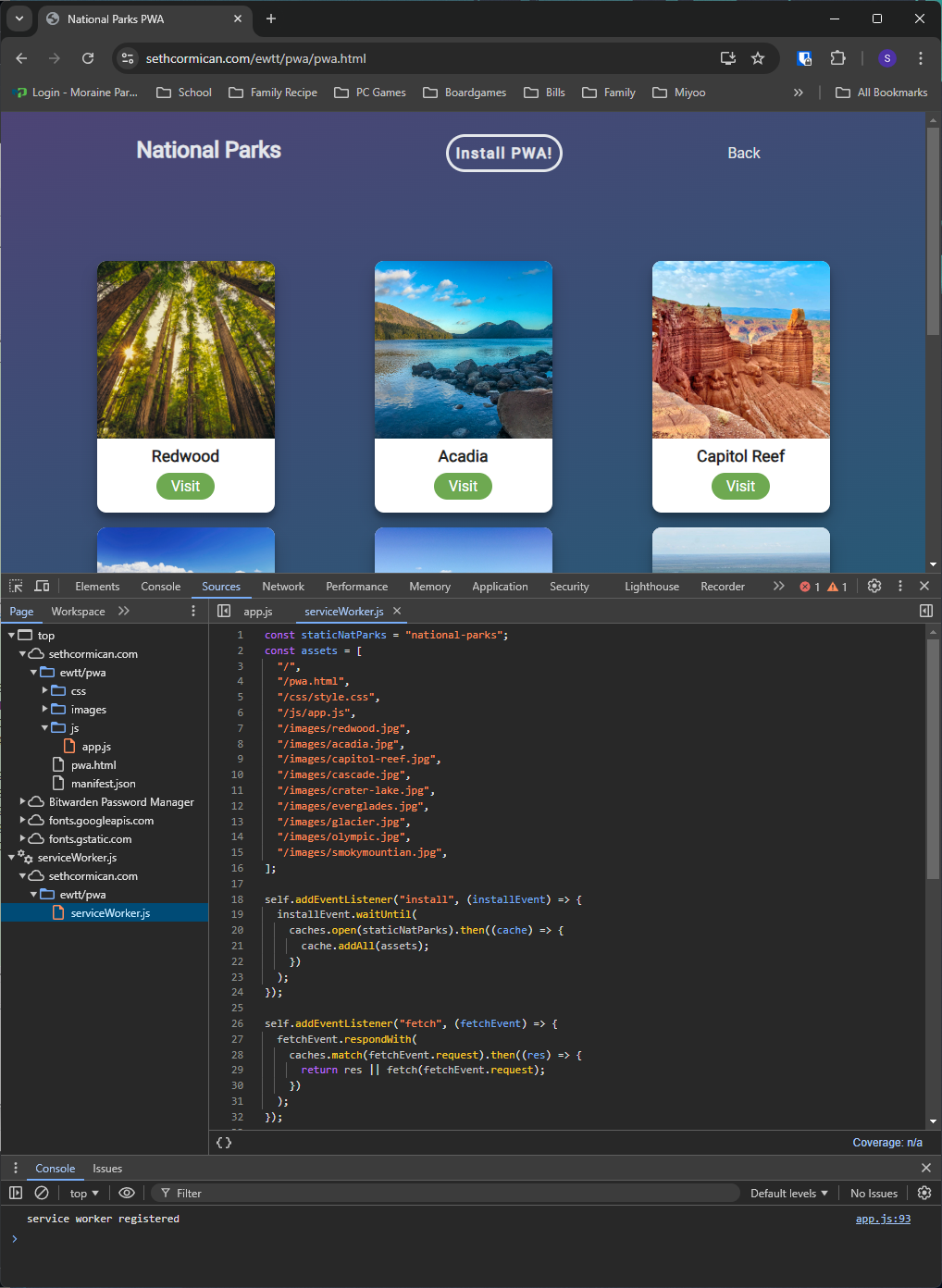
Service workers are an important part of a PWA. These scripts use JavaScript and run in the
background. They act like a proxy server between the web server and web browser because they can
intercept and control network requests. Because of the access service workers provide they only work
on websites with HTTPS. The benefit of using a service worker is that they can cache the web app to
provide faster loading page loading and offline capabilities.
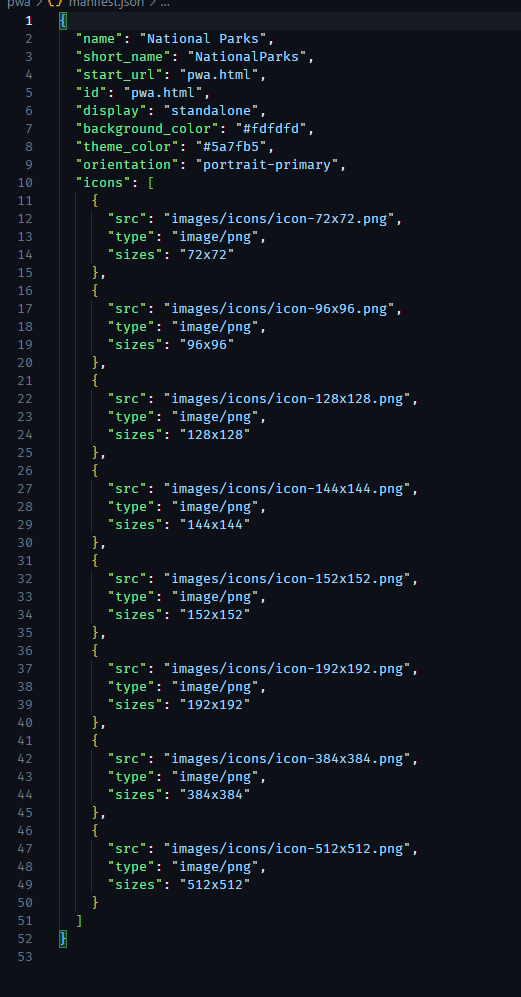
Web App Manifest
The web app manifest is a JSON file that provides information that a browser needs to install a PWA.
The manifest uses different values called members to help create how the PWA appears to users. These
members can help to style the PWA to look like the web version of the app as well as provide icons
that open the PWA. They also help to place the correct size icon for the device that is downloading
the PWA.
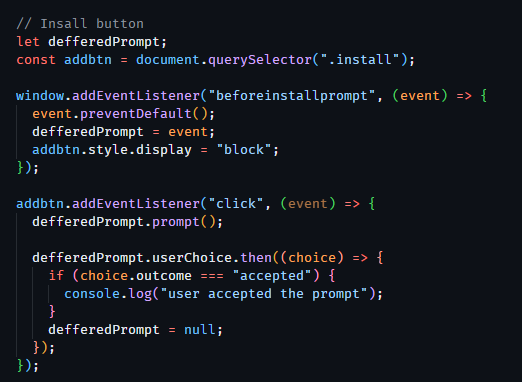
beforeinstallprompt
The beforeinstallprompt helps the browser to detect if the web application is ready to install and
that a user does not have the PWA installed already. It then can notify the user that the web app
can be installed. When I implemented the beforeinstallprompt I added an install button to help the
users know that the web app is installable. The notification in the address bar still pops up to
show the PWA is installable but adding the button lets the user know that it can be installed
without getting in their way too much.
Device of Choice
I decided to test my PWA on an iPhone 12 mini, Windows 11 Desktop PC, and a MacBook Pro. The CSS grid
allowed the images to reduce the amount of columns as the screen size gets smaller. I added a screen
break at 415px that changed the flex-direction of the navigation area to be displayed as a column.
This allowed everything to be spaced better. I also provided a lot of various-sized icons to be
displayed on the different sized devices when PWA is installed.
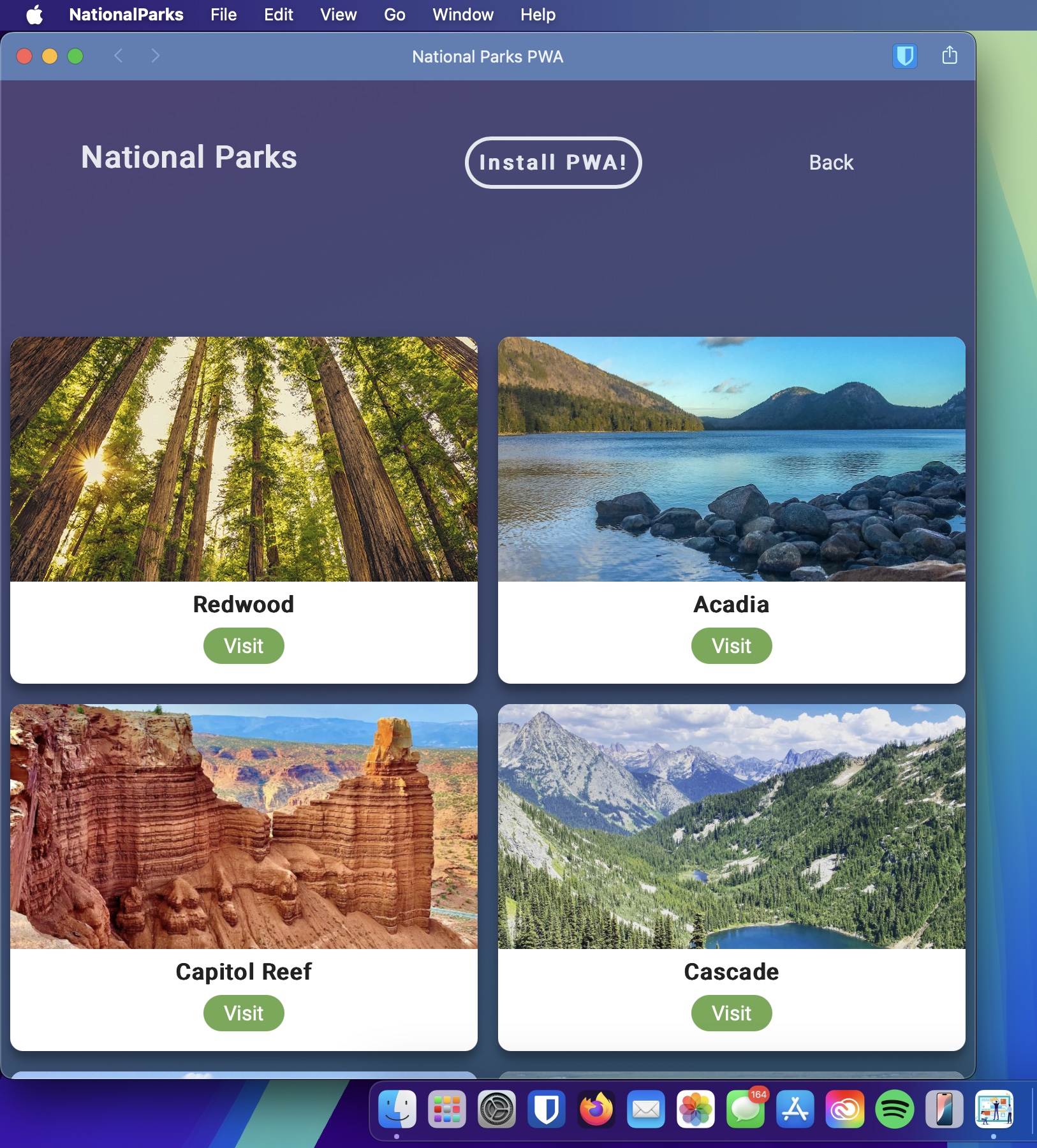
MacBool Pro PWA
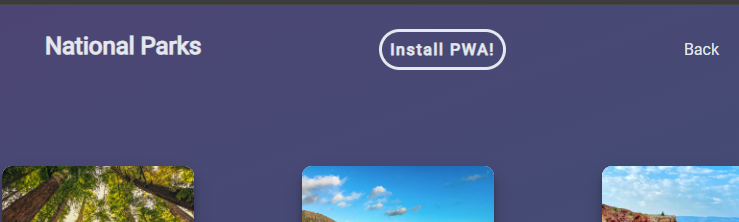
iPhone 12 Mini PWA
SEO Choices
SEO is an important part of any webpage. To better improve my SEO I made sure to include page titles,
a meta description, use alt text for images, and used HTML 5 semantic tags. The alt text helps with
accessibility and the page is also responsive which can help to improve SEO performance.
Reflection
Through learning Module 2 Part 1 I was able to make a web application and turn it into a progressive
web app. It was a challenging task to implement a PWA because it was something I was not familiar
with. After researching the project I was able to implement a manifest JSON file and a service
worker JavaScript file. The service worker provides a way to cache the website, the manifest JSON
provides the information to make the PWA installable. A separate JavaScript file can be used to use
the beforeinstallprompt to detect if a browser has the PWA already installed. I was able to use a
separate JavaScript file with the beforeintallprompt that allowed me to add an install button to be
displayed for the PWA. Having not worked on a project like this before it was helpful to learn how
these different scripts and files are connected to make a PWA.
Resources
https://medium.com/samsung-internet-dev/pwa-series-service-workers-the-basics-about-offline-a6e8f1d92dfd
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Service_Worker_API/Using_Service_Workers
https://medium.com/samsung-internet-dev/pwa-series-the-manifest-file-cheatsheet-459b4a5e2098
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/Manifest
https://www.modyo.com/community/developer-tips/display-a-prompt-to-install-pwas
https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/build-a-pwa-from-scratch-with-html-css-and-javascript/
https://dev.to/mtee/how-do-you-prompt-a-user-to-install-a-pwa-56ef
https://pwa-workshop.js.org/